Explain Different Types of Keys in Database
Keys in Database Management System DBMS. Age can be derived from date of birth where Age is the derived attribute.
Primary Key - The primary key is selected from one of the candidate keys and becomes the identifying key of a table.
. A foreign key is a relationship between columns in two database tables one of which is indexed designed to insure consistency of data eg. If a Super Key does not have any duplicate attribute it is known as a. In a dense index a record is created for every search key valued in the database.
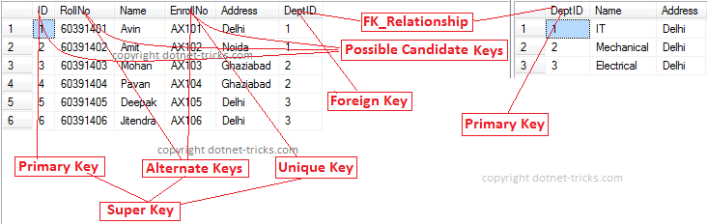
Various Types of Keys in DBMS Candidate Key - The candidate keys in a table are defined as the set of keys that is minimal and can uniquely identify. In this case we have ID and Name Address as Candidate Key we will consider ID Key as a Primary Key as the other key is the combination of more than one attribute. Different Types of Keys in Relational Model.
A database key is said be unique when it has a unique value for each row that is tuple record instance. First Normal Form 1NF Second Normal Form 2NF Third Normal Form 3NF Boyce-Codd Normal Form BCNF Fourth Normal Form 4NF Fifth Normal Form 5NF SQL Concept. SQL provides super key primary key candidate key alternate key foreign key compound key composite key and surrogate key.
Super Key - Super Key is. There can be more than one candidate key in a relation. Alternate key It is also a unique value of the table and generally knows as secondary key of the table.
Types of Keys in a Relational Database. Types of Database Key. Primary Index is an ordered file which is fixed length size with two fields.
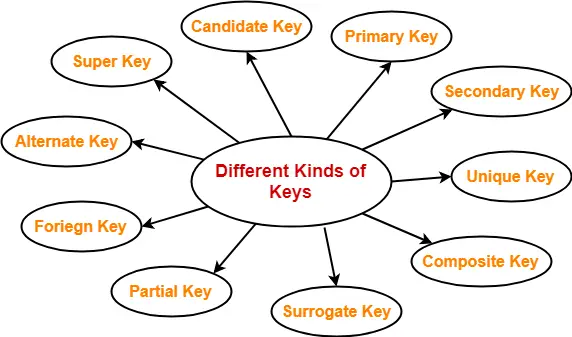
Lets look at each of them separately. Different Types of Keys in DBMS are- Super key Candidate key Primary key Alternate key Foreign key Partial key Composite key Unique key Surrogate key Secondary key. DOB is the stored attribute.
Each record in a CUSTOMER table contains the ID of the. This question hasnt been solved yet Ask an expert Ask an expert Ask an expert done loading. Derived Attributes or stored Attributes.
There are broadly seven types of keys in DBMS. An attribute that can uniquely identify a row and exists in the real world. The first group of keys include unique keys and the second group is non-unique keys.
An attribute that can uniquely identify a. When one attribute value is derived from the other is called a derived attribute. Key provide several types of constraints like column cant store duplicate values or null values.
Keys in DBMS is a set of attributes that can identify each tuple uniquely of the given relation. They are also used to create relationship between different tables. The keys are defined in a table to access or sequence the stored data quickly and smoothly.
A Key is an attribute or a set of attributes in a relation that identifies a tuple record in a relation. Candidate Key Super Key Primary Key. In SQL keys are the set of attributes that used to identify the specific row in a table and to find or create the relation between two or more tables ie keys identify the rows by combining one or more columns.
The primary key cannot be null blank. Candidate keys are those attributes of a relation which have the properties of uniqueness and irreducibly whose explanation is given below. Keys are also used to generate relationship among different database tables or views.
Back to Top So in summary the different types of database keys are. Why we have Keys in DB. In other words a minimal superkey.
Superkey - A set of attributes that uniquely identifies each tuple in a relation. Composite key It is the key which consist of two or more attribute. A primary key is a column of a table or a set of columns that helps to identify every record present in that table uniquely.
Let R be a relation. IV Foreign Key A foreign key is an attribute or combination of attribute in one base table that. Both of these are key fields.
Foreign Key In the fact table the primary key of other dimension table is act as the foreign key. -Explain various types of database keys Super key Candidate key Primary key and Foreign key with your clear definitionsideas and at least one appropriate example for each one of them. The primary Indexing is also further divided into two types 1Dense Index 2Sparse Index.
The primary key is indexed. Of Primary Key - Database designer can use one of the Candidate Key as a Primary Key. Keys make sure to uniquely identify a tables each part or record of a field or combination of fields like Primary Key Foreign Key Super Key Unique Key Candidate Key Composite Key Simple Key compound Alternative Key Non Prime key surrogate natural key.
A key is an attribute or set of attributes in a relation that uniquely identifies a tuple in a relation. The value of the Candidate Key is unique and non-null for every tuple. The objective of this blog is to make you familiar with different types of keys with examples and how they can be used within a database app.
Types of Keys Database supports the following types of keys. A primary key is a one or more fields that uniquely identifies a row in a table. Candidate Key - Similar to a superkey but does not contain a subset of attributes that is itself a superkey.
Every key which has the property of uniqueness can be distinguished as following. The minimal set of attributes that can uniquely identify a tuple is known as a candidate key. The database key types can be broadly grouped into two groups.
Two main types of indexing methods are 1Primary Indexing 2 Secondary Indexing. Summary of the Different Types of Database Keys. For Example STUD_NO in STUDENT relation.
Super key is either a single key or a set of keys which helps in identifying distinct rows in a particular. Different Types of Key in DBMS 1 Super Key. Truncate Drop and Rename query.
Types of Keys in DBMS.

7 Different Types Of Database Keys Explained With Example

Various Types Of Key In Relational Dbms By Rajvi Shah The Startup Medium
Comments
Post a Comment